Introduction to Snake Consumption
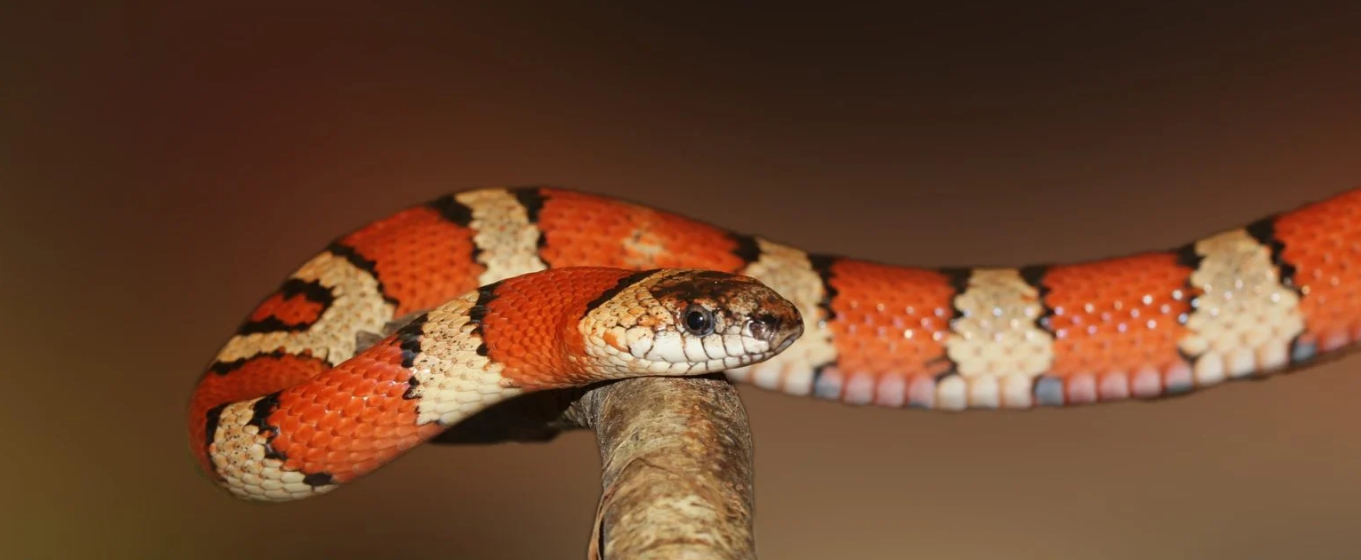
When you think of exotic delicacies, snake meat might not be the first thing that comes to mind. Yet, across various cultures and regions, consuming What eats snakes has a long-standing tradition. From savory soups in Asia to grilled skewers in Africa, these slithery creatures find themselves on dinner plates around the world. But what are the real benefits and potential drawbacks of incorporating snakes into your diet? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of snake consumption—its cultural significance, nutritional value, health implications, and more. Whether you’re curious about trying it or simply want to learn why some people swear by it, this exploration will shed light on all aspects of eating snakes.
Cultural and historical significance of consuming snakes
Snake consumption has deep cultural roots in various societies worldwide. In many Asian countries, such as China and Vietnam, snake meat is considered a delicacy. It often symbolizes strength and vitality.
Historically, indigenous tribes in the Americas have used snakes as vital food sources during harsh winters. They believed that eating snakes could impart their agility and cunning to humans.
In some cultures, snake meat carries medicinal properties. It’s commonly thought to improve one’s health or cure ailments. Traditional medicine practices sometimes include snake blood or fat for healing rituals.
Festivals celebrating snakes also highlight their importance in local cuisines. These events draw attention to regional traditions, fostering a sense of community around shared culinary experiences while preserving historical practices related to hunting and cooking these reptiles.
Nutritional value of snake meat
Snake meat is surprisingly nutritious, often overlooked in discussions about alternative protein sources. It typically contains a high level of protein and low fat content, making it an appealing option for health-conscious individuals.
The nutritional profile can vary depending on the species. For example, python or rattlesnake meat is rich in essential amino acids, which are vital for muscle growth and repair.
Moreover, snake meat provides important vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients support various bodily functions—from energy production to heart health.
When prepared correctly, snake dishes can be both delicious and beneficial to your diet. Exploring this unique source of nutrition expands culinary horizons while offering a sustainable alternative to more conventional meats.
Potential health benefits of eating snakes
Eating snake meat is gaining attention for its potential health benefits. It’s lean, high in protein, and low in fat, making it an excellent option for those looking to maintain muscle while managing weight.
Snake meat is also rich in vitamins and minerals. It contains essential nutrients like iron, which helps transport oxygen in the blood. Additionally, it’s a good source of magnesium, important for various bodily functions including muscle and nerve function.
Some cultures believe that consuming snake can boost energy levels and improve overall vitality. The amino acids found in snake flesh may aid recovery after physical exertion.
Moreover, certain species are thought to have medicinal properties. In traditional medicine practices, snake oil has been used to treat various ailments due to its supposed anti-inflammatory effects.
Exploring these health aspects could open new avenues for culinary enthusiasts and health-conscious eaters alike.
Risks and dangers of consuming snakes
Eating snakes can pose several risks that potential consumers should be aware of. One major concern is the transmission of diseases. Snakes can carry parasites and bacteria, such as Salmonella, which may lead to severe gastrointestinal issues.
Another risk involves improper cooking methods. Under-cooked snake meat can harbor harmful pathogens, putting your health at significant risk. It’s crucial to ensure that the meat reaches a safe temperature before consumption.
Additionally, some species of snake are venomous or toxic when consumed. Eating these types could result in serious poisoning or even death if not correctly prepared by an expert.
Environmental factors also play a role; over-harvesting certain snake populations may disrupt local ecosystems and contribute to biodiversity loss. These aspects highlight the importance of being informed before indulging in this unusual culinary choice.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Snake Consumption
Ethical considerations around snake consumption spark heated debates. Many cultures have long embraced this practice, viewing snakes as a valuable food source. However, the methods of capture and slaughter raise significant concerns.
Wildlife conservationists argue that unsustainable hunting can threaten certain snake populations. Overharvesting disrupts ecosystems and can lead to imbalances in local biodiversity. It’s crucial to consider whether the species consumed is abundant or endangered.
Moreover, animal welfare issues come into play. The conditions under which snakes are raised or hunted often lack humane standards. This raises questions about respect for all living beings and their right to life.
Choosing ethically sourced snakes may help mitigate some of these concerns. Supporting local farms with sustainable practices ensures that consumption does not contribute negatively to environmental health or animal suffering.
Alternative protein sources for those interested in trying snake meat
For those curious about snake meat but seeking alternatives, a variety of protein sources can satisfy adventurous palates.
Insects are increasingly popular worldwide. They’re rich in protein and packed with essential nutrients. Crickets or mealworms can provide an exciting twist to your meals.
Another option is game meats like rabbit or venison. These lean proteins offer unique flavors without the ethical dilemmas some face when considering snake consumption.
Fish is also a fantastic alternative, offering omega-3 fatty acids alongside high-quality protein. Salmon and trout not only taste great but are widely accessible.
Plant-based proteins shouldn’t be overlooked either. Legumes such as lentils and chickpeas deliver substantial nutrition while catering to vegan diets.
Exploring these options allows culinary enthusiasts to enjoy diverse tastes while maintaining a balanced diet without resorting to snakes.
Conclusion: Is eating snakes worth it?
Eating snakes can be a fascinating topic, steeped in cultural significance and nutritional value. For those adventurous enough to try it, the unique flavors and textures of snake meat may add an intriguing element to their diet. The potential health benefits, including high protein content and low-fat levels, make it an interesting alternative for protein-seekers.
However, this choice does not come without risks. Consuming improperly prepared snake meat can lead to foodborne illnesses or exposure to parasites. Ethical considerations also arise around the treatment of snakes within both farming practices and wild populations.
For individuals looking to diversify their diets with alternative proteins, there are plenty of options available that do not involve consuming snakes. From plant-based proteins like beans and lentils to other meats such as chicken or fish, many alternatives exist.
What eats snakes is worth it depends on personal preference and values regarding nutrition, ethics, and sustainability. It’s vital for anyone considering this culinary adventure to weigh these factors carefully before taking the plunge into snake consumption.